Determine and Fix Your VPN Tunnel’s Maximum MTU
Why This is Necessary
Your VPN connection is up, but web sites (HTTP) and SSH will not load/connect or are very very slow. This condition is known as black-holing. This is common with PPPoE or other links where the MTU is less than 1500, often due to Path MTU Discovery (PMTUD) failure when required ICMP error packets are dropped by a firewall.
Overhead for OpenVPN over a PPPoE Link
The standard PPPoE MTU is 1492 bytes, which is the maximum packet size you can transmit without fragmentation.
The below calculations assume OpenVPN is configured using proto udp4 and data-ciphers AES-256-GCM (the default directives).

Total Overhead:
Outer IP/UDP (28) + OpenVPN (32) + Inner IP/TCP (40) = 100 bytes
Maximum Payload (MSS):
PPPoE MTU (1492) - overhead (100) = 1392 bytes
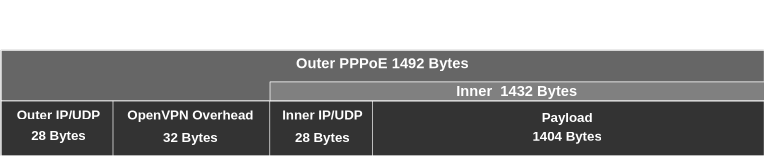
Total Overhead:
Outer IP/UDP (28) + OpenVPN (32) + Inner IP/UDP (28) = 88 bytes
Maximum Payload:
PPPoE MTU (1492) - overhead (88) = 1404 bytes
Test the Link
Find the Client’s IP Address
You can find the client’s IP address in the OpenVPN server log. The client name is typically what you named your client config file (e.g., client-thinkpad.ovpn). Search for the client’s IP address using the journalctl command—it will be in the pool returned IPv4=xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx entry.
sudo journalctl -u openvpn@server.service | grep client-thinkpad | grep 'pool returned IPv4'
Oct 09 17:57:59 mars ovpn-server[4043]: client-thinkpad/<your IP>:54988 MULTI_sva: pool returned IPv4=10.8.0.2, IPv6=(Not enabled)
Use ping to Find Maximum Payload Size
From the OpenVPN server, ping the client. Based on the calculation above, we expect a payload of 1404 bytes to pass, since ping (ICMP) is encapsulated UDP segment.
ping -M do -s 1405 10.8.0.2
PING 10.8.0.2 (10.8.0.2) 1405(1433) bytes of data.
ping: local error: message too long
ping: local error: message too long
ping: local error: message too long
ping: local error: message too long
ping: local error: message too long
^C
--- 10.8.0.2 ping statistics ---
5 packets transmitted, 0 received, +5 errors, 100% packet loss, time 4072ms
ping -M do -s 1404 10.8.0.2
PING 10.8.0.2 (10.8.0.2) 1404(1432) bytes of data.
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=128 time=55.5 ms
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=2 ttl=128 time=57.4 ms
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=3 ttl=128 time=54.9 ms
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=4 ttl=128 time=62.1 ms
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=5 ttl=128 time=62.4 ms
1412 bytes from 10.8.0.2: icmp_seq=6 ttl=128 time=51.0 ms
--- 10.8.0.2 ping statistics ---
6 packets transmitted, 6 received, 0% packet loss, time 5008ms
rtt min/avg/max/mdev = 51.022/57.211/62.434/4.030 ms
The maximum payload size was 1404 bytes. This confirms the outer link’s MTU of 1492.
1404 (ICMP Data) + 20 (IP Header) + 8 (ICMP Header) = 1432 (Maximum Inner MTU)
Maximum Segment Size (MSS)
The Linux Kernel will attempt to automatically determine an optimal MSS based on the interface MTU. For a typical Ethernet-based network with a MTU of 1500, The Kernel internally adjusts the MSS to 1400 (1500 - 100 overhead = 1400). This automatic adjustment often causes black-holing on a PPPoE link where the maximum outer MTU is lower (1492).
With a PPPoE MTU of 1492 the maximum MSS would be 1392 (1492 PPPoE MTU - 100 overhead = 1392 MSS). When the OpenVPN server is behind a firewall, the connection to it is typically Ethernet. Therefore, the Linux Kernel is unaware that the connection to the Internet is over a PPPoE link. That is why you need to manually set the inner MTU with the tun-mtu 1432 directive. Which sets the tun0 interface to 1432 allowing the Kernel to determine the correct optimal MSS.
Total Packet for PPPoE MTU 1492
Outer IP/UDP |
OpenVPN Overhead |
Inner IP/TCP |
TCP Payload (MSS) |
|---|
Setting the inner tunnel MTU tun-mtu to 1432 ensures the inner packet does not exceed the limit.
tun-mtu(1432) - Inner IP/TCP Headers(40) = MSS 1392
Configure OpenVPN
Setting the Inner Tunnel MTU
The maximum size for the inner IP packet (the traffic inside the tunnel, which is what the tun-mtu setting controls) must be the largest size that, when fully encapsulated by OpenVPN, does not exceed your outer MTU, which is 1492 for PPPoE.
From our ping test above we found that the maximum payload was 1404.
Maximum Inner MTU: 1404 + 20 IP Header + 8 UDP/ICMP Header = 1432
Add tun-mtu 1432 directive to the /etc/openvpn/server.conf file and restart the server.
sudo nano /etc/openvpn/server.conf
sudo systemctl restart openvpn.service
⚠️ Special Consideration: OpenVPN Data Channel Offload DCO and mssfix directive
When clients use the newer, high-performance OpenVPN Data Channel Offload (DCO) kernel module (common on modern Windows and Linux distributions), explicitly setting the mssfix directive in the client configuration file is strongly discouraged.
Including –mssfix directive, increases the overhead form 6.7% to 11%, effecting the maximum throughput for your VPN by 4.7%.
The Conflict
Server’s Role: The server correctly pushes the optimal MSS using
tun-mtu 1432.Kernel’s Calculation: The client operating system kernel uses this MTU of 1432 to automatically calculate the optimal MSS of 1392 (1432 - 40).
DCO Interference: When the client explicitly sets
mssfix 1392, the DCO layer interprets this as a ceiling and aggressively applies an internal, conservative safety margin (often additional 64 bytes for ciphers like AES-256-GCM).Result: This results in an unnecessarily low negotiated MSS (e.g., 1328 instead of 1392), which increases packet overhead and reduces throughput, this can an issue especially on slow links like DSL.
The Windows 11 OpenVPN client log file will show if DCO is enable.
2025-10-28 10:43:25 us=109000 OpenVPN 2.6.13 [git:v2.6.13/5662b3a8eb9e5744] Windows [SSL (OpenSSL)] [LZO] [LZ4] [PKCS11] [AEAD] [DCO] built on Feb 17 2025
2025-10-28 10:43:25 us=109000 Windows version 10.0 (Windows 10 or greater), amd64 executable
2025-10-28 10:43:25 us=109000 dontlibrary versions: OpenSSL 3.4.1 11 Feb 2025, LZO 2.10
2025-10-28 10:43:25 us=109000 DCO version: 1.2.1
The Recommendation
Do not use mssfix in the client configuration when the client supports DCO and the server is pushing tun-mtu.
iptables Configuration: Clamp MSS from Local Network (10.10.0.0/24)
Clamp MSS for VPN traffic
This is not mandatory; a host on the the local network will send an initial SNC exchange with the MSS (maximum segment size) MSS it can support, based on the MTU of the interface the host is on. This is just another way to insure packets do not get segmented and is good practice on any VPN network.
Set the --set-mss option to 1392 for a PPPoE link.
Ensure tun0 is your tunnel interface. If not, replace it. Use the ip address command to confirm your interface name before setting this rule.
# Replace tun0 with your tunnel interface name.
iptables -t mangle -A POSTROUTING -p tcp -o tun0 --tcp-flags SYN,RST SYN -j TCPMSS --set-mss 1392
Test
Web sites should now load.
Verify the Inner Tunnel MTU is set to 1432 (the value set by tun-mtu).
* Linux
ip a show tun0
18: tun0: <POINTOPOINT,MULTICAST,NOARP,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1432 qdisc fq_codel state UNKNOWN group default qlen 500
link/none
inet 10.8.0.1/24 scope global tun0
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 fe80::21a6:c3bf:7783:e4c8/64 scope link stable-privacy
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
* Windows 11
netsh interface ipv4 show subinterfaces
MTU MediaSenseState Bytes In Bytes Out Interface
---------- --------------- ------------ ------------ -------------
4294967295 1 0 112725 Loopback Pseudo-Interface 1
65535 5 0 0 OpenVPN Wintun
1500 1 193137021 49070504 Wi-Fi
1500 5 0 0 Bluetooth Network Connection
1500 5 0 0 OpenVPN TAP-Windows6
1500 5 0 0 Local Area Connection* 1
1432 1 107411217 20356825 OpenVPN Data Channel Offload <------- this line
1500 5 0 0 Local Area Connection* 2
1500 1 255297 1201796 vEthernet (WSL)
Use tcpdump and look for the MSS option in the SYN packets; it should be 1392 in both directions.
sudo tcpdump -i tun0 -nl | grep mss
[sudo] password for user:
tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v[v]... for full protocol decode
listening on tun0, link-type RAW (Raw IP), snapshot length 262144 bytes
22:29:30.600135 IP 10.8.0.2.57698 > 10.10.0.204.8006: Flags [S], seq 1352582822, win 65535, options [mss 1392,nop,wscale 8,nop,nop,sackOK], length 0
22:29:30.600173 IP 10.8.0.2.50937 > 10.10.0.204.8006: Flags [S], seq 256465994, win 65535, options [mss 1392,nop,wscale 8,nop,nop,sackOK], length 0
22:29:30.600294 IP 10.10.0.204.8006 > 10.8.0.2.57698: Flags [S.], seq 3389130376, ack 1352582823, win 64240, options [mss 1392,nop,nop,sackOK,nop,wscale 7], length 0
22:29:30.600300 IP 10.10.0.204.8006 > 10.8.0.2.50937: Flags [S.], seq 1966382350, ack 256465995, win 64240, options [mss 1392,nop,nop,sackOK,nop,wscale 7], length 0
22:30:01.980196 IP 10.10.0.204.8006 > 10.8.0.2.57698: Flags [S.], seq 3389130376, ack 1352582823, win 64240, options [mss 1392,nop,nop,sackOK,nop,wscale 7], length 0
^C
1796 packets captured
1796 packets received by filter
0 packets dropped by kernel
Use iperf3 to test the max MSS. If running iperf3 from the client use the -R option. A zero bitrate returned means you have exceeded the maximum MSS.
iperf3 -R --dont-fragment -M 1392 -c devel
Connecting to host devel, port 5201
Reverse mode, remote host devel is sending
[ 5] local 172.26.44.37 port 35492 connected to 10.10.0.150 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate
[ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 1.50 MBytes 12.6 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 2.12 MBytes 17.8 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 2.00 MBytes 16.8 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 1.38 MBytes 11.5 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 1.50 MBytes 12.6 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 5.00-6.00 sec 1.12 MBytes 9.44 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 6.00-7.00 sec 896 KBytes 7.34 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 7.00-8.00 sec 896 KBytes 7.34 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 8.00-9.00 sec 896 KBytes 7.34 Mbits/sec
[ 5] 9.00-10.00 sec 768 KBytes 6.29 Mbits/sec
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr
[ 5] 0.00-10.06 sec 13.5 MBytes 11.3 Mbits/sec 16 sender
[ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 13.0 MBytes 10.9 Mbits/sec receiver
iperf Done.
billf@thinkpad-wsl ~> iperf3 -R --dont-fragment -M 1393 -c devel
Connecting to host devel, port 5201
Reverse mode, remote host devel is sending
[ 5] local 172.26.44.37 port 46274 connected to 10.10.0.150 port 5201
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate
[ 5] 0.00-1.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 1.00-2.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 2.00-3.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 3.00-4.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 4.00-5.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 5.00-6.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 6.00-7.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 7.00-8.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 8.00-9.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
[ 5] 9.00-10.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec
- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - -
[ ID] Interval Transfer Bitrate Retr
[ 5] 0.00-10.04 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec 5 sender
[ 5] 0.00-10.00 sec 0.00 Bytes 0.00 bits/sec receiver
iperf Done.